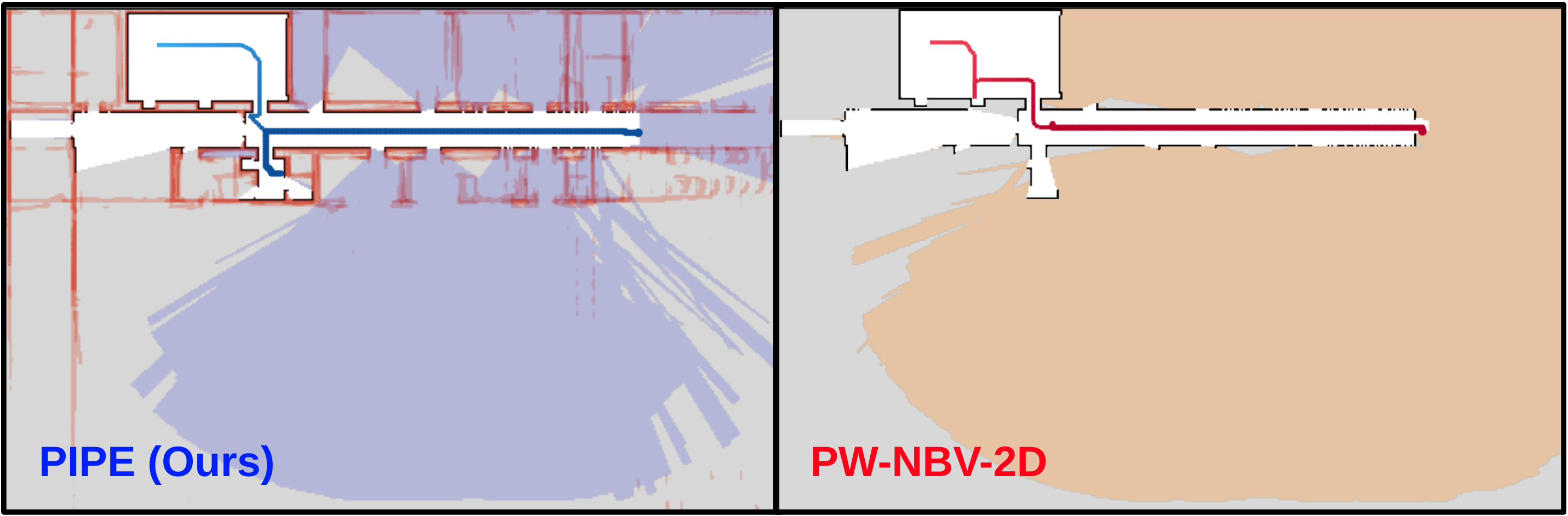
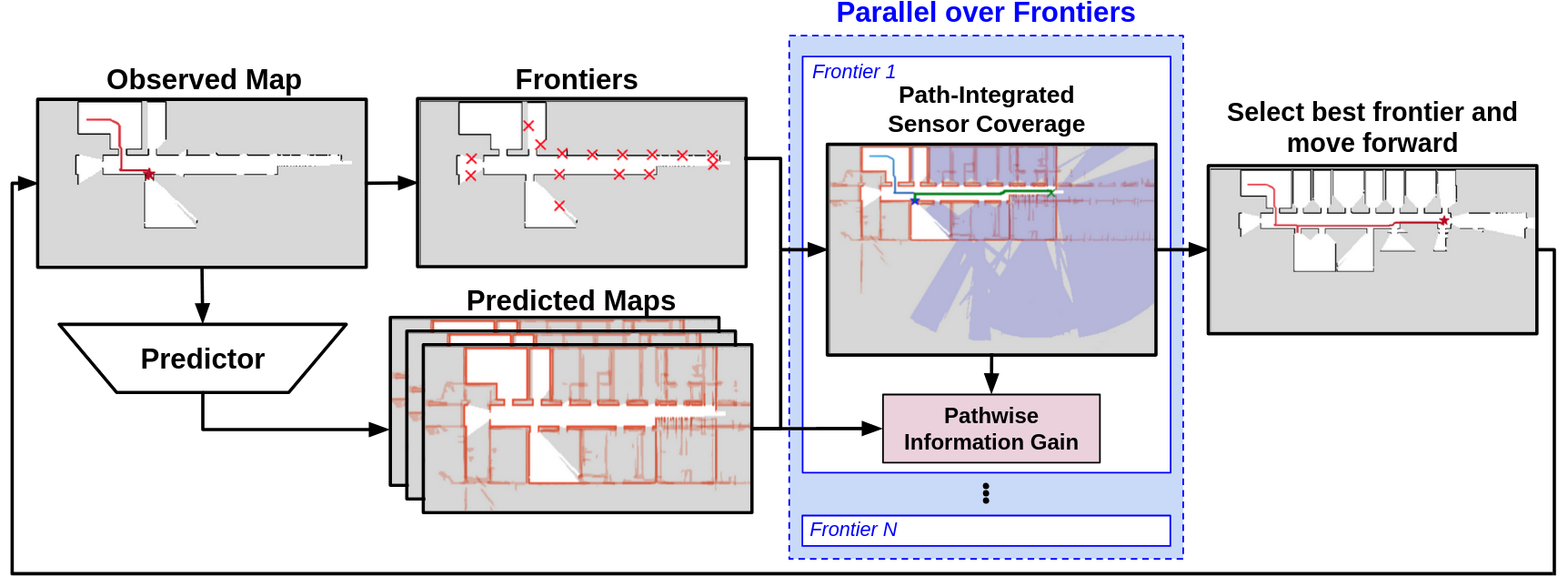
Insight 1: Fast computation of pathwise sensor coverage
The core component of PIPE planner is to estimate information gain of each frontier, by integrating cumulative sensor coverage (estimated by raycasts) along each path. But this is computationally expensive. How do we compute the cumulative information gain efficiently?
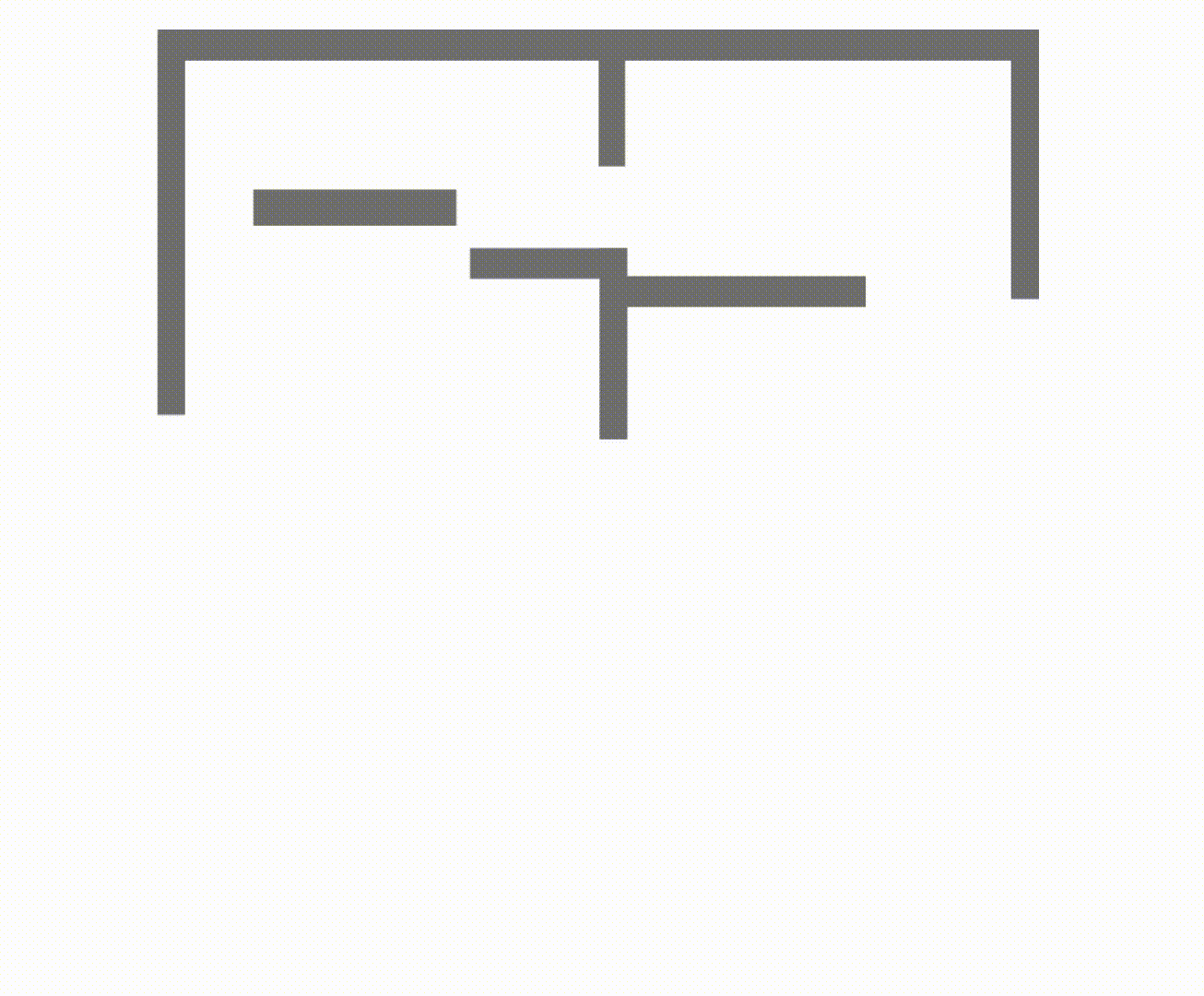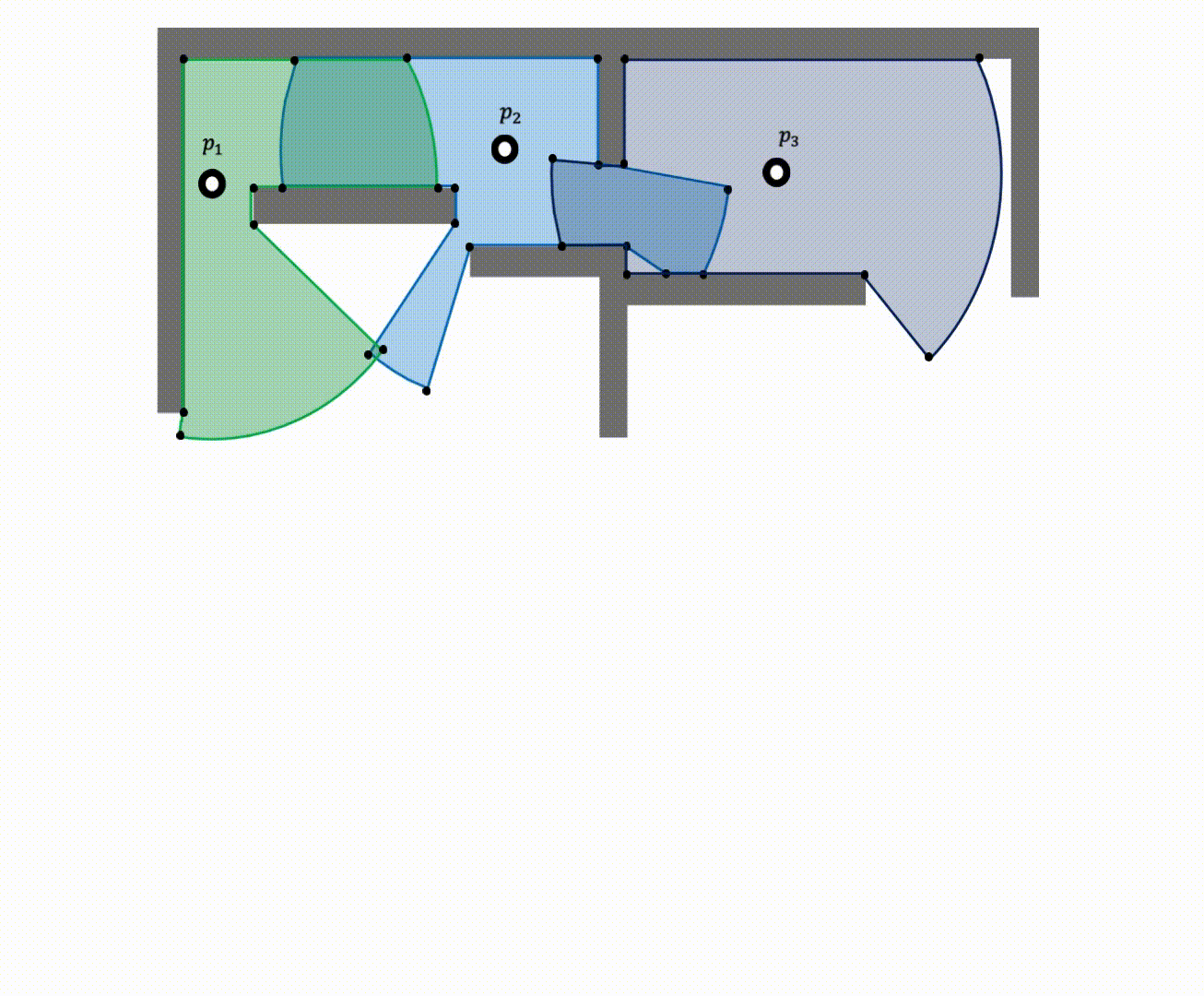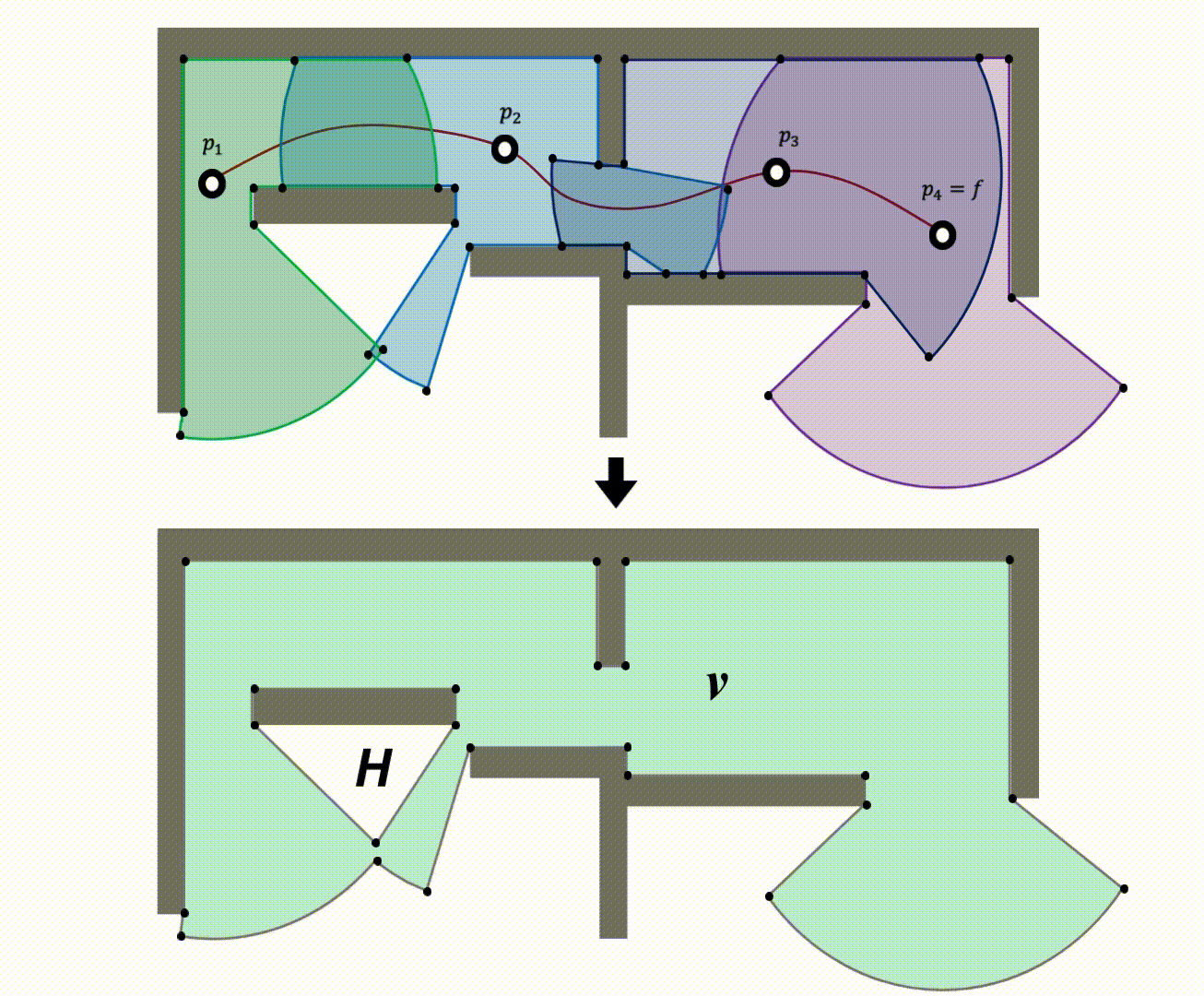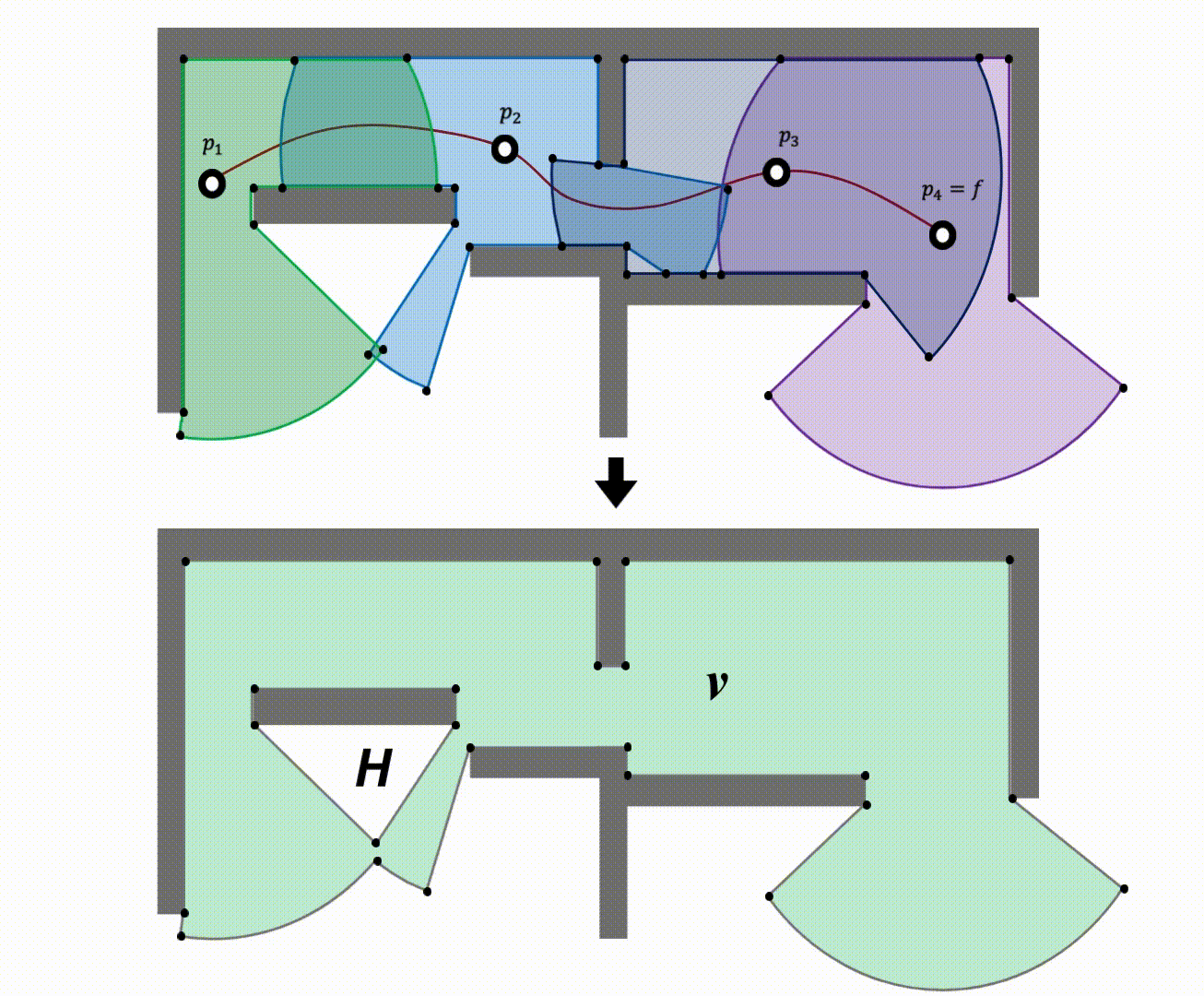
Rather than performing a flood fill operation seprately for each raycast-generated polygon and then taking the union of the visibility masks, we first merge the raycast-generated polygons into one and apply a single flood fill operation to the merged polygon. We leverage computational geometry to address union of multiple nonconvex raycasted polygons (trapped regions or holes).